Intro to AD 1
Hi guys
Welcome back :).
What is AD?
Active Directory (AD) is a database and set of services that connect users with the network resources they need to get their work done. It contains critical information about your environment, including what users and computers there are and who is allowed to do what. For example, the database might list 100 user accounts with details like each person’s job title, phone number and password. It will also record their permissions.
So always make sure each person is who they claim to be (authentication), usually by checking the user ID and password they enter and allow them to access only the data they are allowed to use (authorization).
Why should we know about AD?
Active Directory is a massive and complex attack surface that has long been a prime target for criminals seeking valuable privileges and data.
AD services.
The main service is Domain Services, but Active Directory also includes Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), Certificate Services, or AD CS, Federation Services (AD FS) and Rights Management Services (AD RMS). Each of these other services expands the product’s directory management capabilities.
- Lightweight Directory Services has the same codebase as AD DS, sharing similar functionalities, such as the application program interface. AD LDS, however, can run in multiple instances on one server and holds directory data in a data store using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol.
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is an application protocol used to access and maintain directory services over a network. LDAP stores objects, such as usernames and passwords, in directory services, such as Active Directory, and shares that object data across the network.
- Certificate Services generates, manages and shares certificates. A certificate uses encryption to enable a user to exchange information over the internet securely with a public key.
- Active Directory Federation Services authenticates user access to multiple applications – even on different networks – using single sign-on (SSO). As the name indicates, SSO only requires the user to sign on once, rather than use multiple dedicated authentication keys for each service.
- Rights Management Services control information rights and management. AD RMS encrypts the content, such as email or Microsoft Word documents, on a server to limit access.
AD structure.
The top-level container is the forest. Within forests are domains, and within domains are organizational units (OUs):
- A forest is a collection of one or more Active Directory domains that share a common logical structure, directory schema (class and attribute definitions), directory configuration (site and replication information), and global catalog (forest-wide search capabilities). All domains in the same forest ae linked automatically.
- A domain is a partition of a forest which include some functions:
- Global (inside the forest) user identity.
- Replication.
- Trust relationships.
- Authentication.
- Organizational units is a subdivision within AD into which you can locate users, groups, computers, and other organizational units.
Now let’s set up our AD.
After installing your WindowsServer, Log in to the Administrator account, Open Server Manager to set some configurations. So, Follow the following steps:
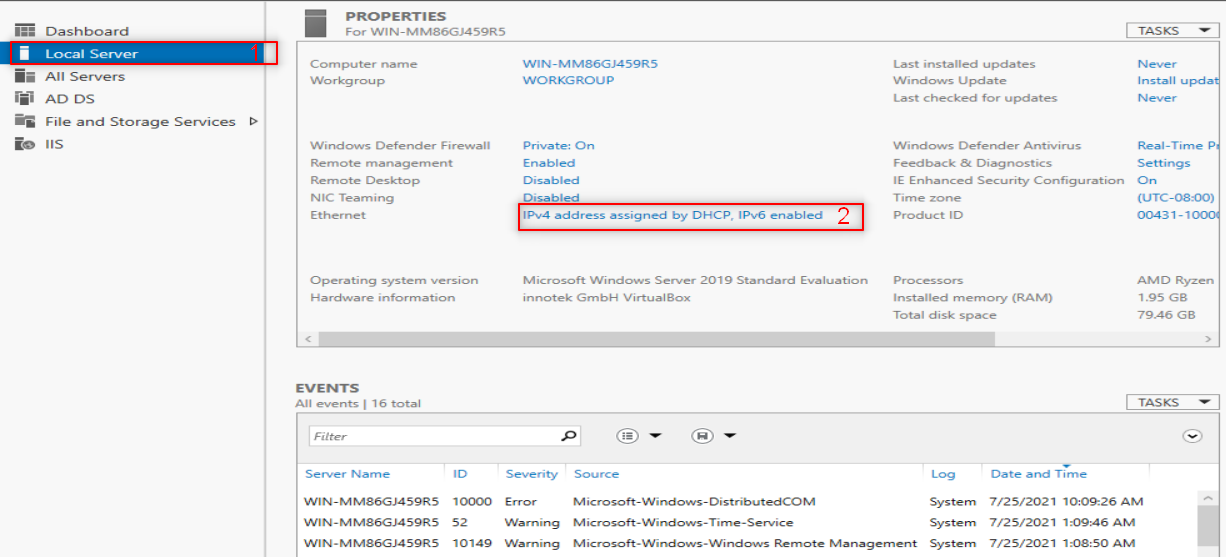
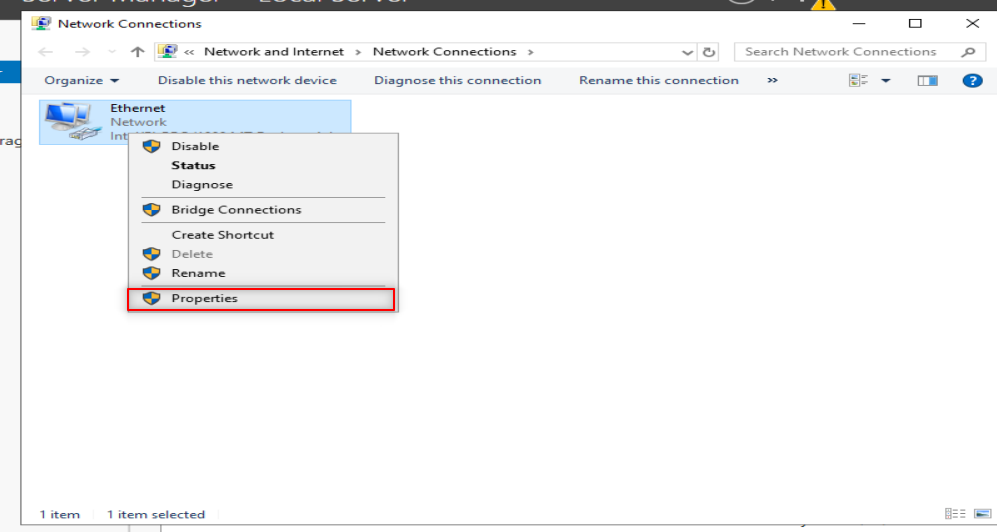
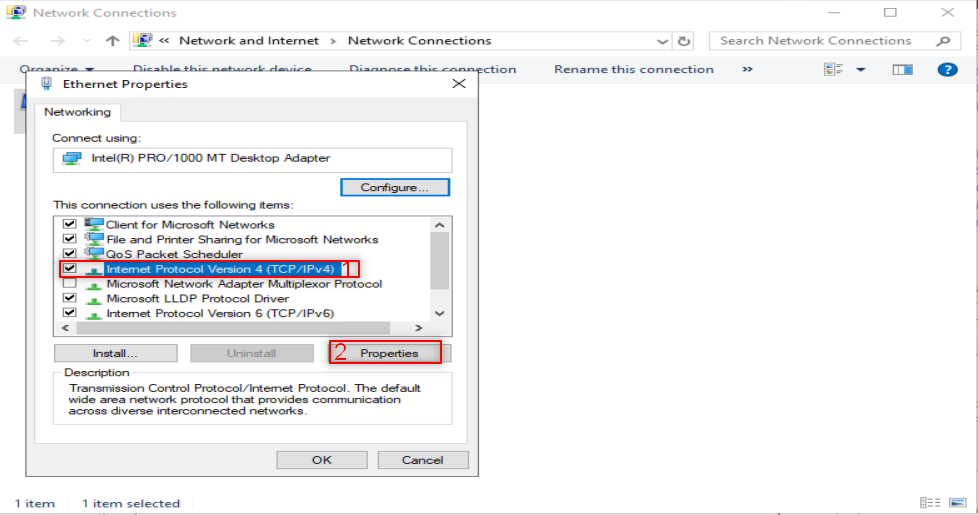
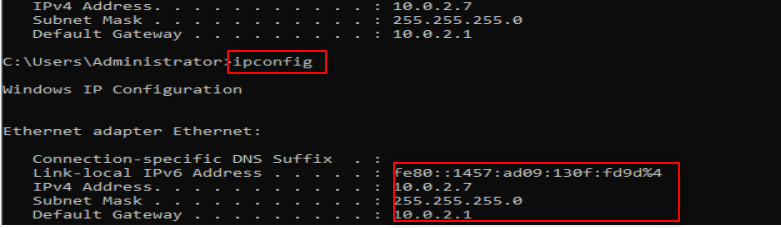
Make sure to put DNS to your IP or localhost.
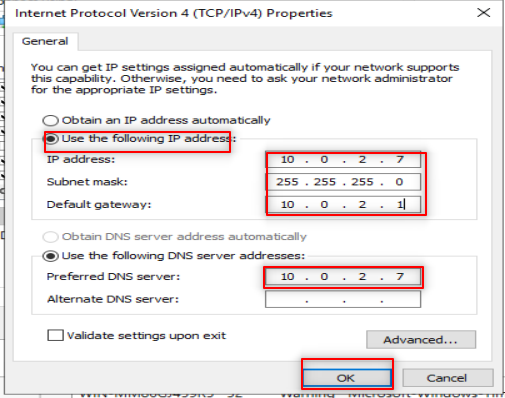
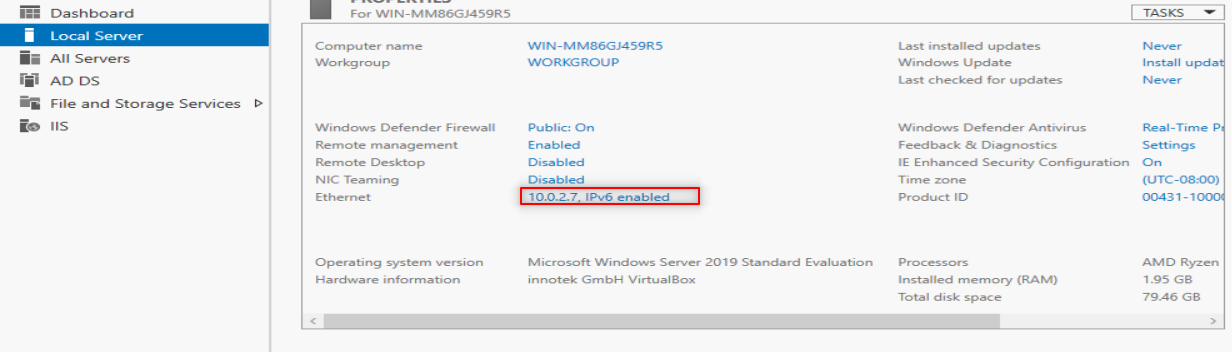
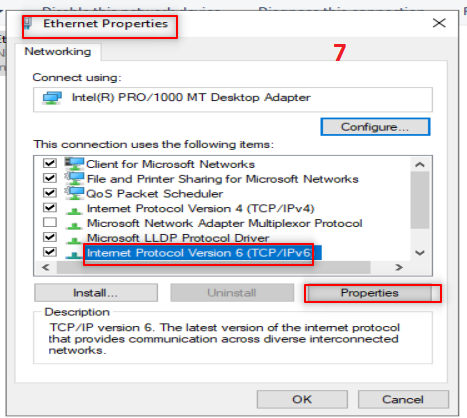
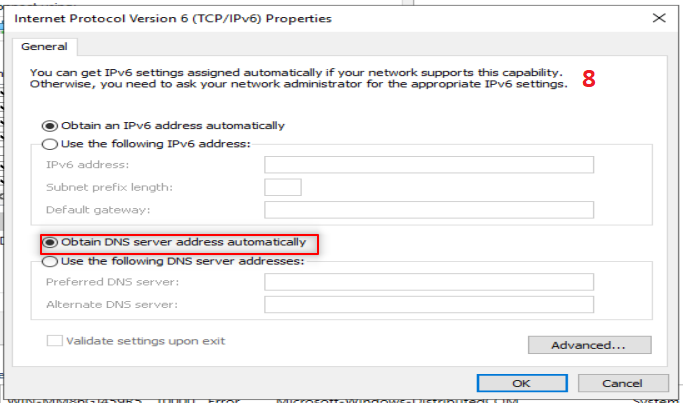
Then we going to add AD feature. So, Follow the following steps:
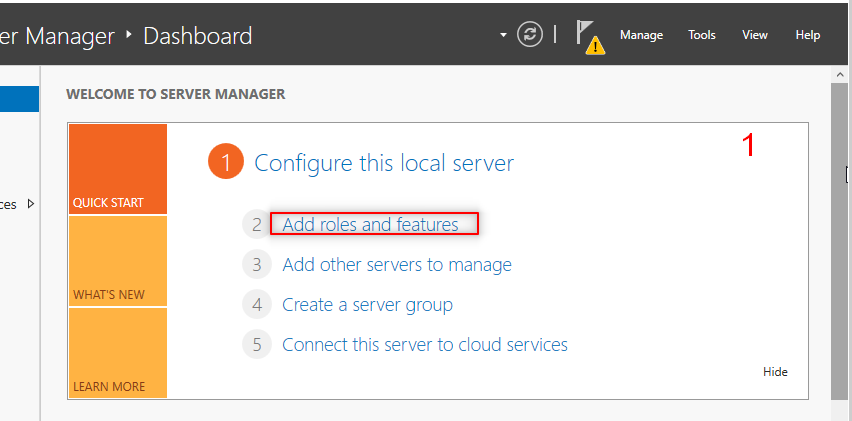
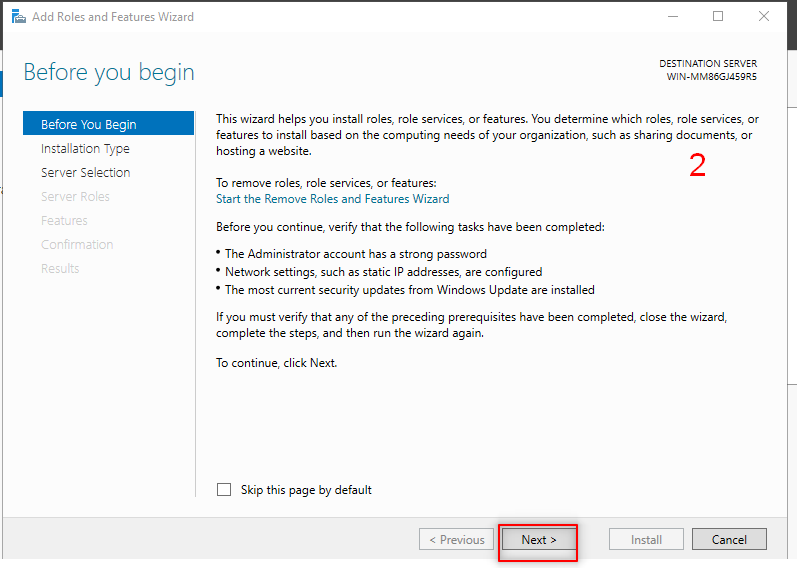
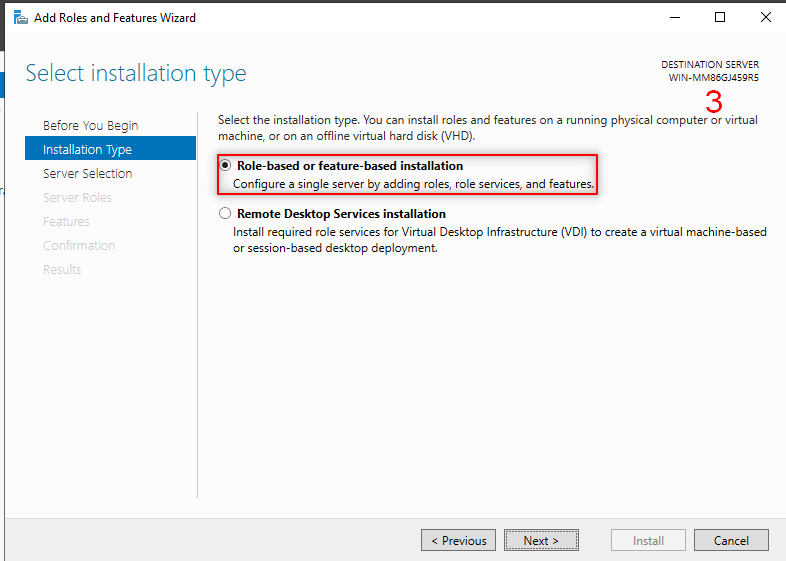
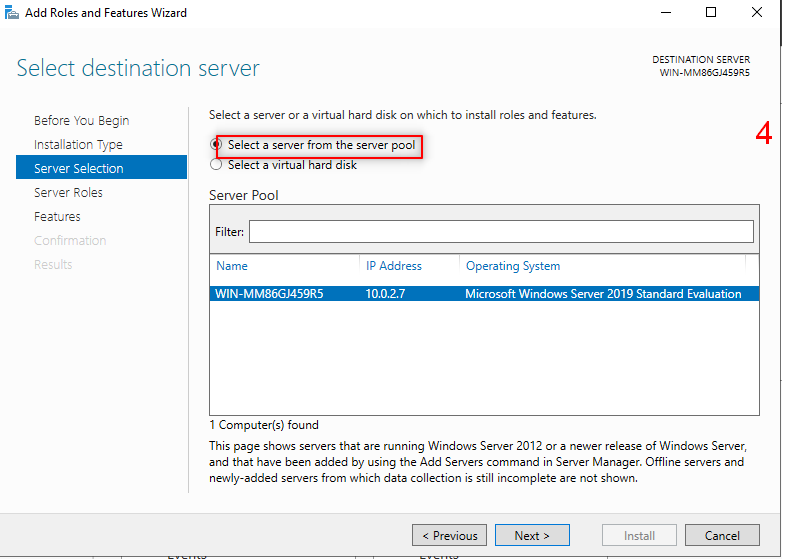
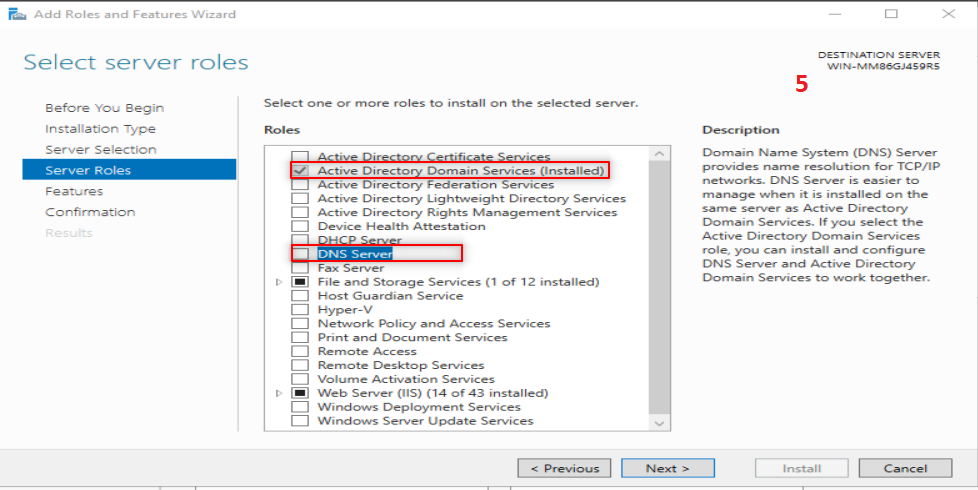
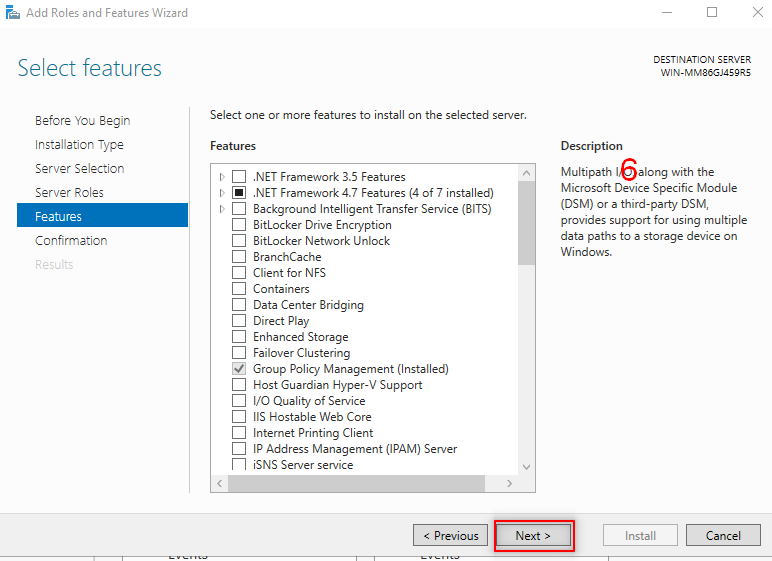
Now, it is time to make our first forest. So, Follow the following steps:
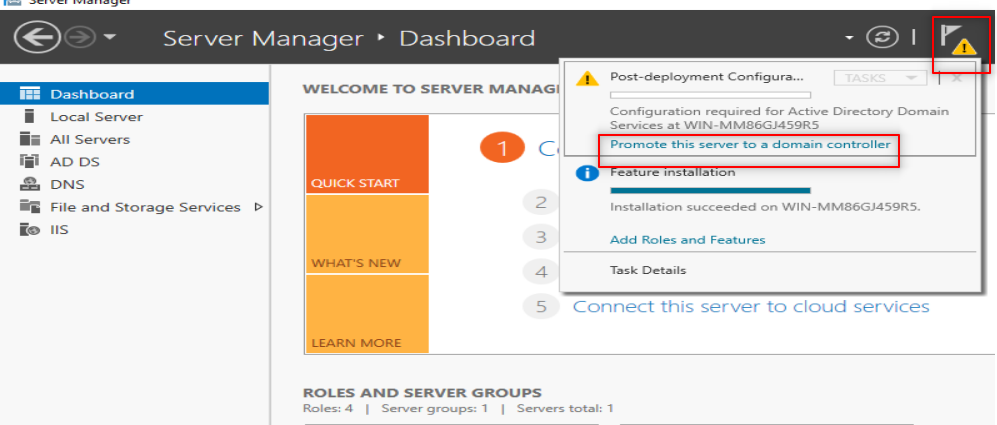
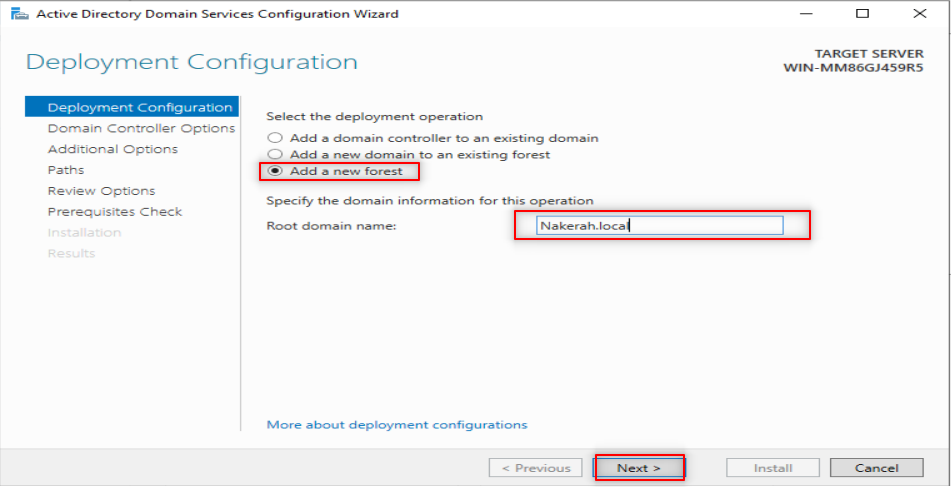
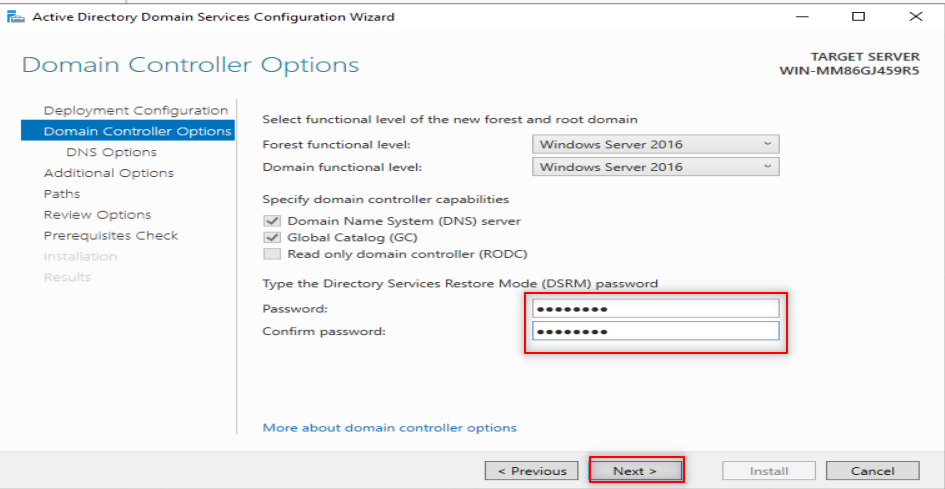
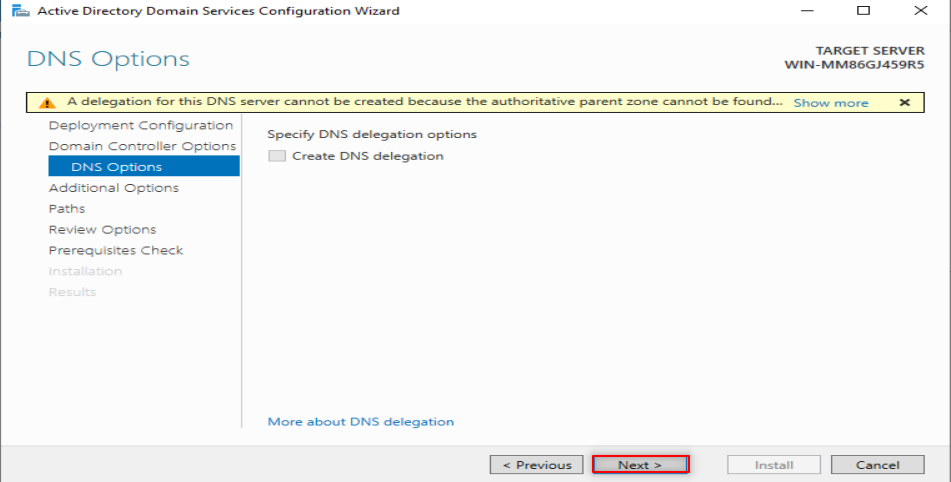
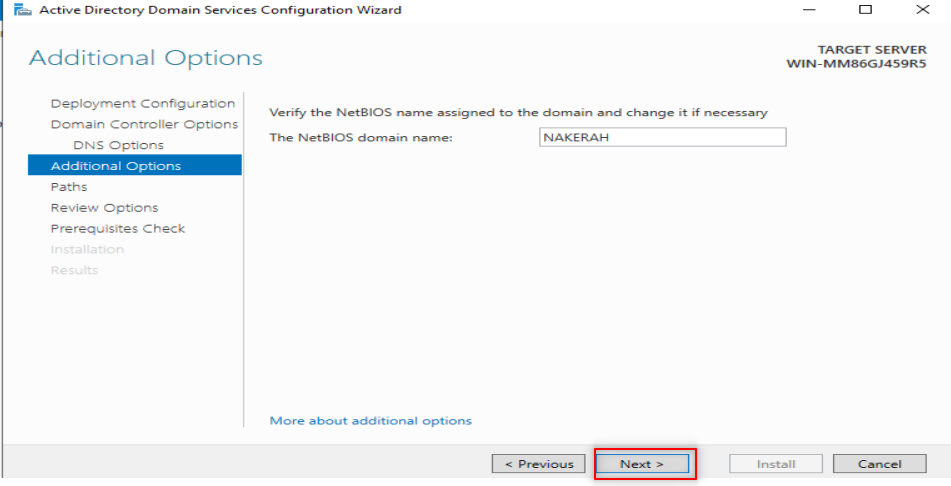
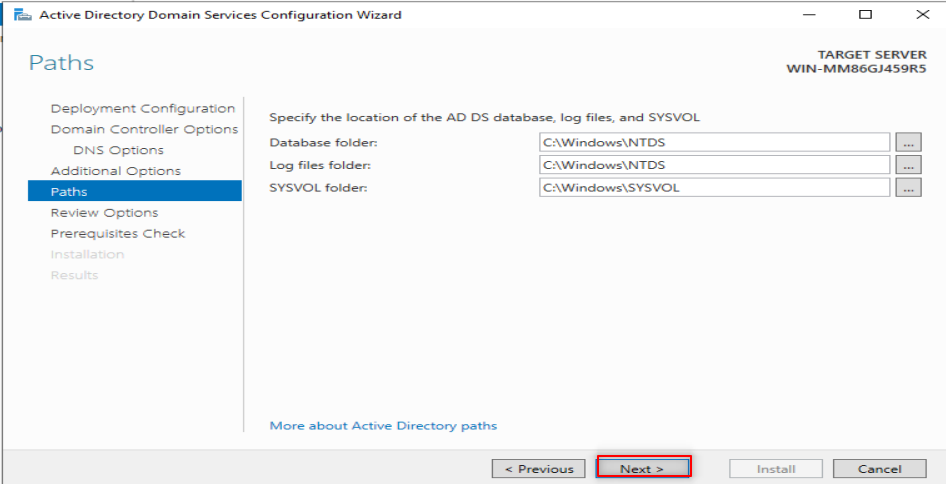
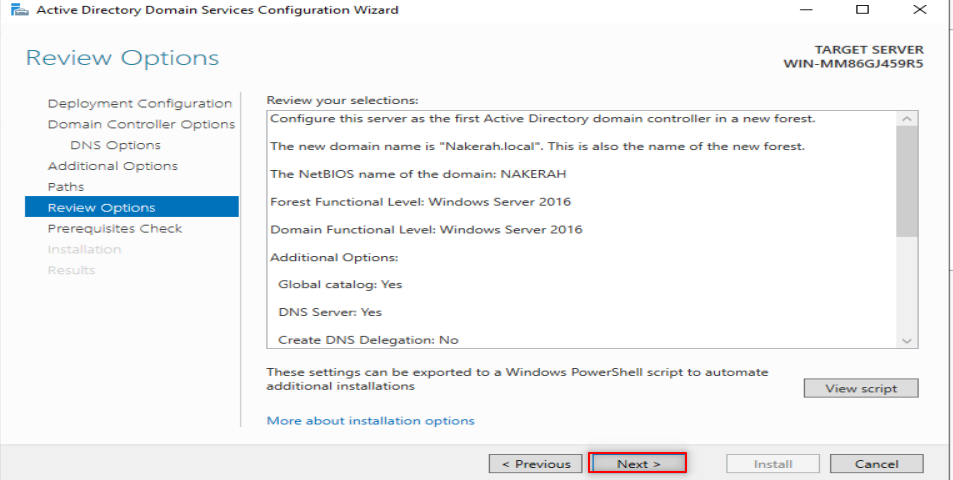
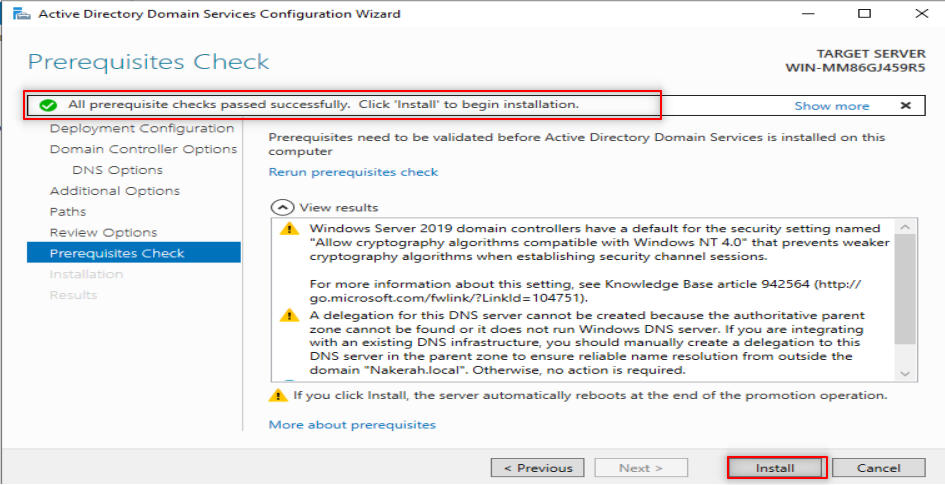
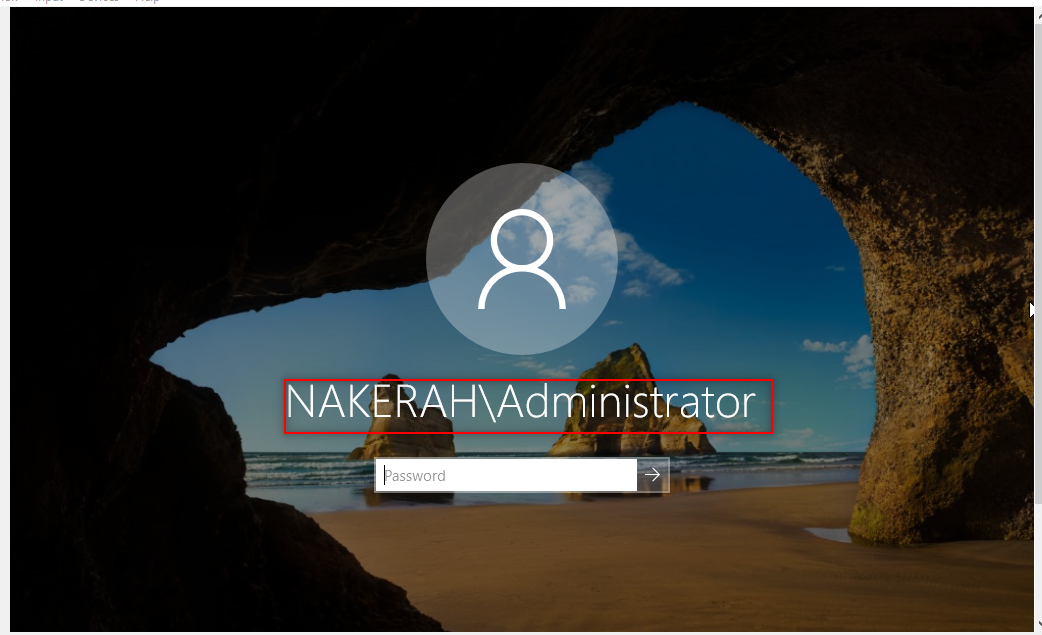
Now, it is time to configure our DNS. So, Follow the following steps:
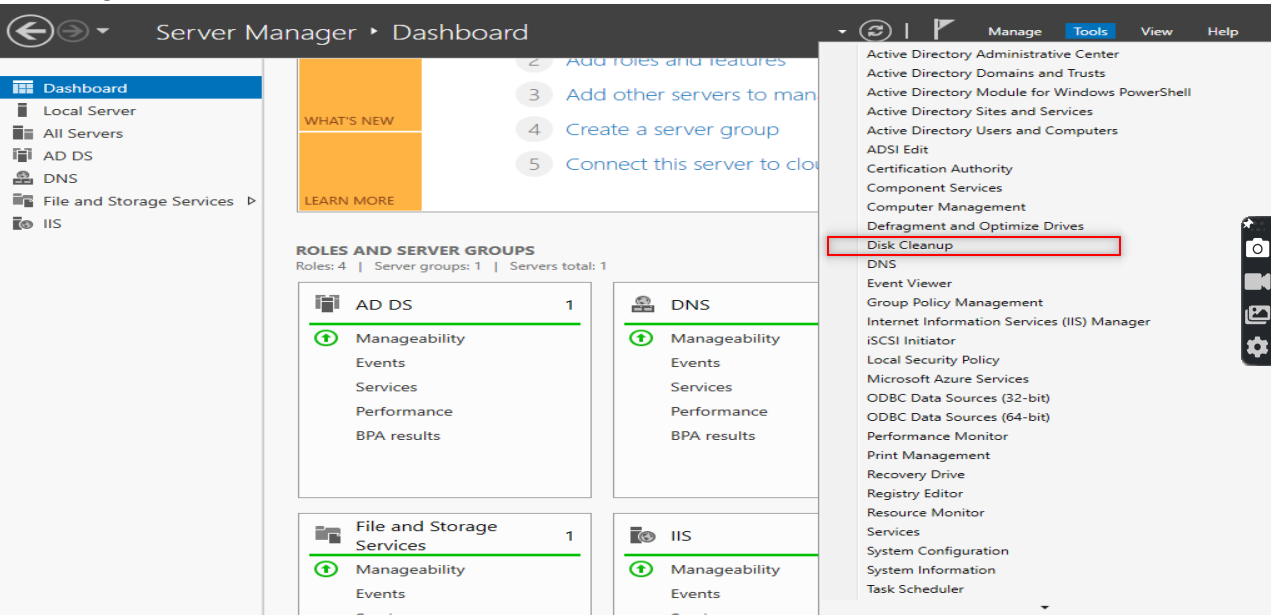
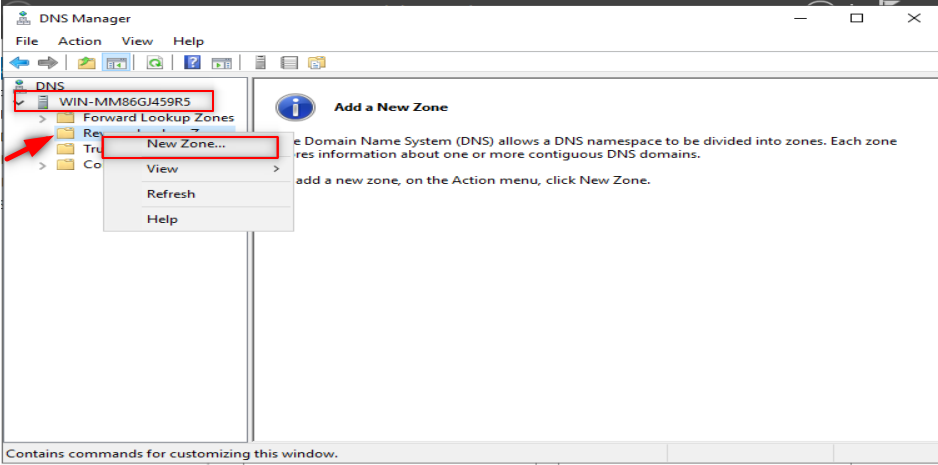
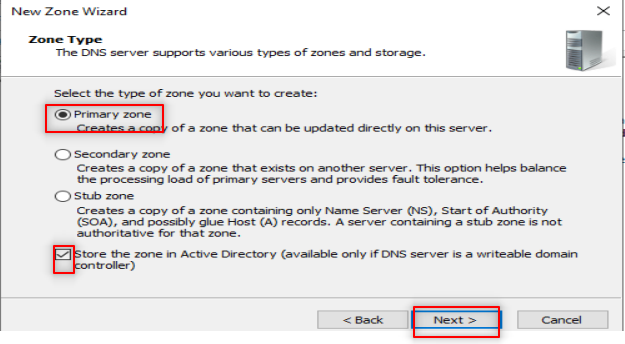
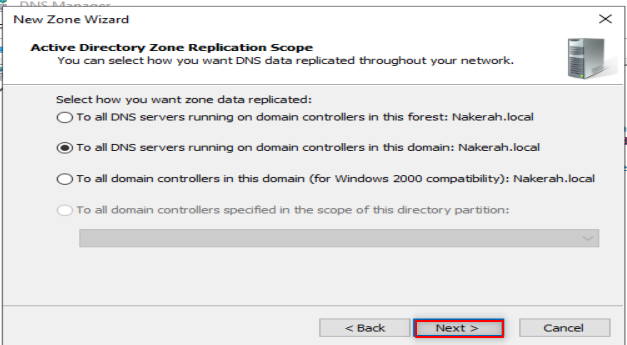
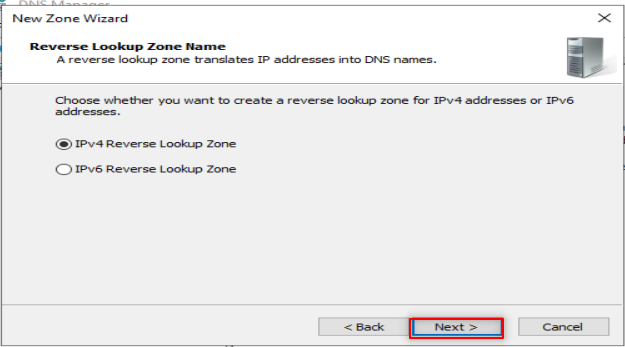
Make sure to put only the first three octets of your IP.
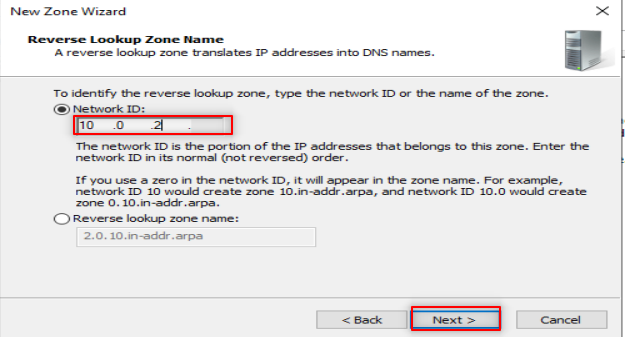
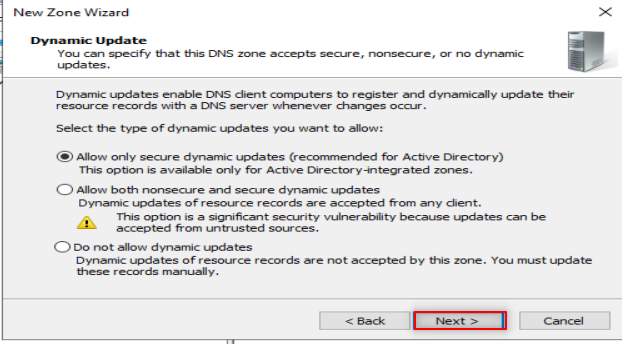
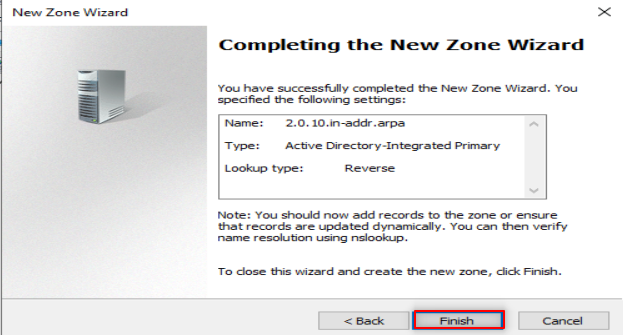
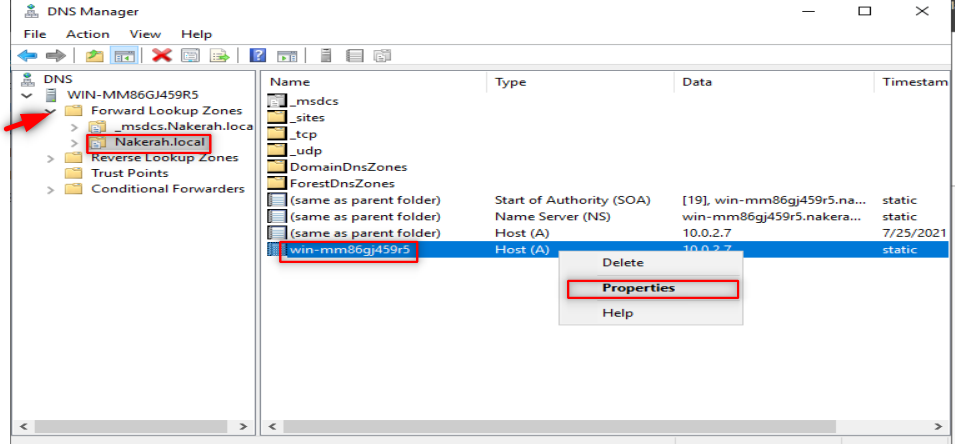
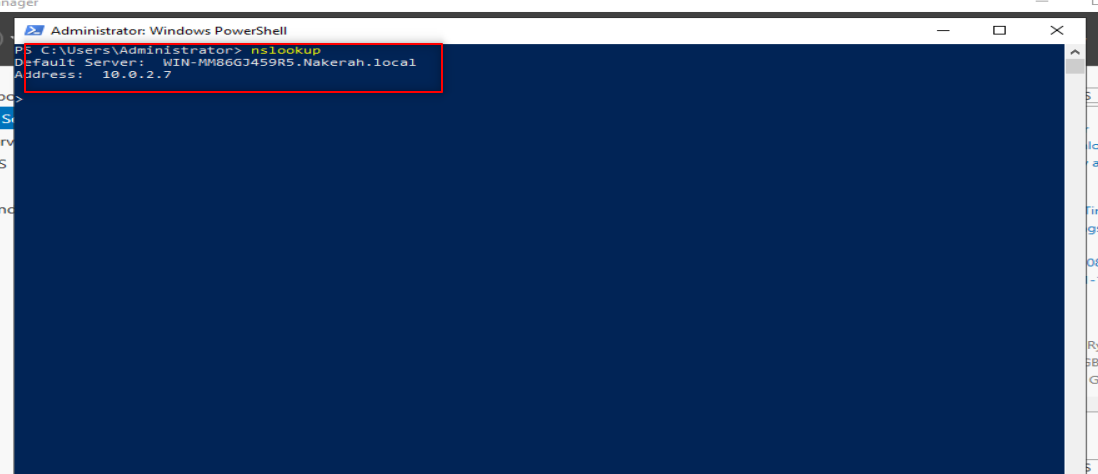
Check your DNS with nslookup , it is supposed you get a similar output.
Our environment is ready now. So see you next time.
